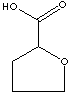
| 2-TETRAHYDROFUROIC ACID | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 16874-33-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | ||
| FORMULA | C5H8O3 | |
| MOL WT. | 116.12 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Tetrahydro-2-furoic acid; Tetrahydrofuran-2-carboxylic acid; | |
| 2-Tetrahydrofuran formic acid; | ||
|
DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear to yellowish liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | 237 - 243 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.17 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Soluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT |
139 C |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. |
|
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Furan; One of a class of heterocyclic aromatic compounds characterized by
five-membered ring structure consisting of four CH2 groups and one oxygen atom.
The simplest furan compound is furan itself; a clear, volatile and mildly toxic
liquid; melts at -86 C, boils at 32 C, insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol
and ether. In the absence of inhibitors, it may form peroxides and and accumulate peroxides
which may explode when subjected to heat or shock. It may discolor on exposure
to air. This material is hazardous when peroxide levels are concentrated by
distillation or evaporation. It can be stabilized with BHT. It can be obtained from wood oils. It is used as a solvent as well as
in the synthesis of furfural and other organic compounds. It is converted to
more important solvent, tetrahydrofuran by hydrogenation. Niitro-substituted
furan derivatives are used as biocides or fungicides to inhibit bacterial
growth. Sulfur-substituted furan derivatives are used as flavouring agents.
Furfural (Furfuraldehyde), a derivative of furan, is a viscous, colorless
liquid that has a pleasant aromatic odor; upon exposure to air it turns dark
brown or black; boils at about 160 C; soluble in ethanol, ether and somewhat in
water. It is commonly used as a solvent. Furfural is the aldehyde of pyromucic
acid; it has properties similar to those of benzaldehyde. It is prepared
commercially by dehydration of pentose sugars obtained from cornstalks and
corncobs, husks of oat and peanut, and other waste products. The major
application of furfural is being use as a feedstock for furfuryl alcohol. The
most commercial quantity of furfuryl alcohol is used in the production of thermosetting furan resin
and furan cement, strong adhesive, in which the furan ring is an integral part of
the polymer chain providing highly resistance to chemicals. Furfural is used as
a solvent for refining lubricating oils and butadiene extraction. It is used as a fungicide and
weed killer. It is used in
the production of tetrahydrofuran (THF), saturated form of furan. THF is one of the most
polar ethers. It is used as an important industrial solvent recognized for its
unique combination of useful properties. It is a colorless, volatile
cycloaliphatic (5-membered) ether with a characteristic odor; boiling point at
66 C; soluble in water and organic solvents. THF is unstable at room temperature
due to possibility of peroxide formation; stabilized sometimes with BHT. Its unhindered oxygen
atom carries two unshared pairs of electrons - a structure which favors the
formation of coordination complexes and the solvation of cations. THF is made
also by eliminating water from 1,4-butanediol. THF is used as an useful chemical
intermediate especially as a starting materials for the preparation of
nylon.
Furoic acid, furancarboxylic acid, is a white to off-white crystalline powder; monoclinic crystals in water solution; soluble in ether and alcohol; melts at 130 C (sublimes at melting point); boils at 230 C. There are two isomers at 2 or 3 position. 2-Furoic acid is called pyromucic acid. It is used as a preservative and bactericide and as a starting material of numerous furoate esters. Its derivatives are widely used as flavouring agents, in medicinal preparations and in biological research. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to yellowish liquid | |
|
PURITY |
99.0% min |
|
|
WATER |
0.5% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 200kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 22-24/25 | ||